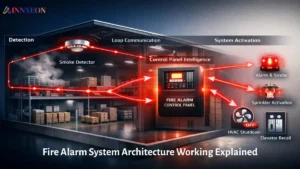
Fire alarm systems have evolved dramatically over the past decade. Today’s design approaches focus not just on detecting fire, but on intelligence, connectivity, efficiency and safety for people and property. Engineers across industries are adopting new technologies and frameworks that improve accuracy, reduce false alarms and integrate seamlessly into modern buildings and smart infrastructure.
In this deep-dive article, we will explore the latest trends in fire alarm system design, explain why they matter, and how engineers are using them to build smarter safety systems.
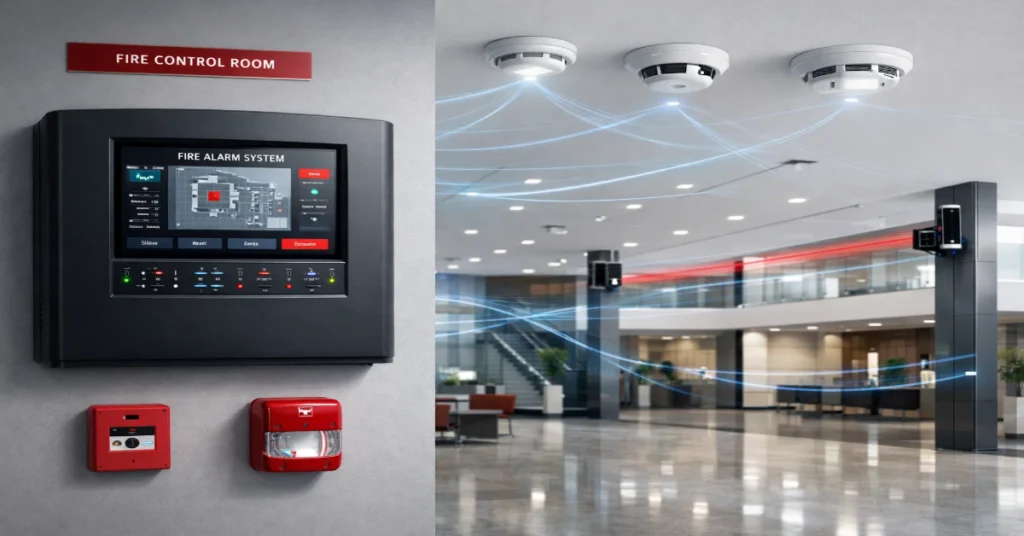

By the end, you will have a clear understanding of key design principles shaping fire alarm engineering in 2025 and beyond.
1. Intelligent & AI-Driven Detection Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a transformative role in fire alarm design today. Instead of simply reacting to smoke or heat, intelligent systems analyse patterns over time and differentiate between harmless signals (like cooking smoke) and genuine emergencies.
Why This Matters
- AI systems improve detection accuracy.
- They significantly reduce false alarms, which otherwise disrupt operations and emergency services.
- Predictive analytics anticipates fire risks before they escalate.
How It Works
Modern fire panels equipped with AI use machine learning models to interpret data from multiple sensors and historical patterns. These systems learn what is “normal” in a space and only signal an alarm when multiple factors match real fire conditions.
This shift toward proactive detection increases safety and dovetails with smarter maintenance strategies, as engineers can receive early notifications of failing components or sensors.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) & Connected Infrastructure
In 2025, connectivity is no longer optional for fire alarm systems; it’s standard. IoT integration connects detection units, panels and control systems across facilities.
Core Advantages
- Real-time Alerts: Managers receive instant notifications on mobile devices or control dashboards.
- Remote Monitoring: Systems can be monitored from anywhere, enabling quick responses to detected risks.
- Centralised Control: Especially useful in campuses or multi-building sites.
IoT-enabled fire alarm networks allow sensors to communicate with each other and other building systems. This deep connectivity supports predictive maintenance, intelligent alerts and advanced data analytics, giving engineers a holistic view of building safety.
3. Wireless & Hybrid Fire Alarm Systems
Wireless technology is no longer seen as a workaround; it’s a trend that offers flexibility, scalability and cost savings.
Why Designers Prefer Wireless
- Quick Installation: Reduces wiring complexity and labour costs.
- Scalability: Easy to add or reposition detectors without major rewiring.
- Ideal for Retrofits: Perfect for historic buildings or sites where invasive wiring is impractical.
In hybrid systems, wireless detectors work alongside wired backbone infrastructure to offer reliability where needed while also benefiting from wireless flexibility.
4. Multi-Sensor Detection Technologies
Traditional smoke detectors rely on a single input, typically smoke or heat. Modern designs use multi-sensor detection technologies that combine signals such as smoke, heat, carbon monoxide (CO) and more.
Benefits of Multi-Sensor Systems
- They can differentiate between real fires and environmental changes (e.g., steam or dust).
- They reduce the likelihood of false alarms and improve early detection.
By analysing a range of variables simultaneously, multi-sensor detectors enhance system intelligence, accuracy and reliability, especially in complex environments like kitchens, factories or warehouses.
5. Advanced Detection Technologies: VESDA, Beam & Thermal Imaging
Cutting-edge solutions extend beyond conventional sensors to deliver very early fire detection and improved coverage.
Very Early Smoke Detection Apparatus (VESDA)
- Uses aspirating technology to sample air before visible smoke appears.
- Ideal for data centres, clean rooms and high-value storage.
Optical Beam Smoke Detectors
- Detect smoke over large open spaces using light beams.
- Common in warehouses and industrial facilities.
Infrared & Thermal Imaging
- Tracks temperature changes visually and identifies abnormal heat patterns before smoke forms.
- Offers proactive fire detection, not just reactive alerts.
These advanced technologies strengthen the ability to protect diverse spaces effectively, reducing the window between ignition and detection.
6. Cloud-Based Monitoring & Centralised Management
Cloud integration is one of the most transformative trends in fire alarm system design.
How It Enhances Fire Safety
- Central access to all system logs and alerts.
- Remote troubleshooting and diagnostics.
- Scalable oversight across multiple facilities.
Cloud platforms also support compliance reporting, analytics dashboards and historical trend analysis, helping engineers make data-driven safety decisions and meet auditing requirements more easily.
7. Integration With Building Management Systems (BMS)
Fire alarm systems today are rarely standalone. Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS) allows fire safety measures to coordinate with HVAC, access control, lighting, elevators and emergency communication systems.
Functional Benefits
- Automatic HVAC shutdown to prevent smoke spread.
- Controlled evacuation lighting and exit signage coordination.
- Enhanced facility-wide safety automation.
This level of integration supports smarter, faster responses during emergencies, improving both safety and operational resilience.
8. Edge Computing & Local Decision Making
Edge computing refers to processing data at the source instead of relying entirely on cloud servers.
Why It’s Important
- Faster processing of critical fire alarm data.
- Reliable performance even during network outages.
- Reduced dependency on centralised systems.
This trend helps ensure systems continue functioning when connectivity is compromised, making them ideal for mission-critical facilities.
9. Cybersecurity for Connected Fire Alarm Systems
As fire alarm systems become more connected and cloud-integrated, cybersecurity becomes essential.
Common Security Features
- Encrypted communications between devices.
- Authentication protocols to prevent unauthorised access.
- Regular over-the-air updates to strengthen defences.
Security-focused design ensures that safety systems themselves are protected from tampering or cyberattacks, which is crucial when they interface with building networks and management platforms.
10. Sustainable & Inclusive Fire Alarm Designs
Modern systems incorporate eco-friendly materials and intuitive alert mechanisms for individuals with special needs.
Sustainability Trends
- Use of non-toxic materials and energy-efficient components.
- Reduced electrical consumption through smart standby modes.
Inclusivity Enhancements
- Visual alerts for the hearing impaired.
- Tactile or vibration notifications for the visually impaired.
These designs ensure fire alarm systems support all occupants and align with modern environmental standards.
The Future of Fire Alarm System Design
Fire alarm system design in 2025 is increasingly smart, connected, predictive and people-centric. By incorporating AI, IoT, cloud technologies, advanced sensors and inclusive features, engineers are building systems that not only detect fire but also prevent it and guide responses.
Trends such as wireless systems, cloud monitoring, multi-sensor detectors, BMS integration, cybersecurity and sustainability define the future of fire safety. Organizations that adopt these innovations will deliver higher levels of safety, efficiency and compliance while meeting the expectations of modern building owners, occupants and regulatory authorities.
Whether you are a building owner, safety engineer, facility manager or fire protection professional, staying informed about these trends will help you plan, design and implement fire alarm systems that are reliable, resilient and ready for tomorrow.
Read Also: The Hidden Challenges of Upgrading Fire Alarm Systems in Occupied Buildings
Read Also: Why a Factory Replaced Its Fire Alarm Panel Mid-Project