Industrial environments such as refineries, chemical plants, oil and gas terminals and pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities often contain flammable gases, combustible particulates or volatile vapors. These areas are classified as hazardous zones and are governed by strict safety directives like ATEX (Europe), IECEx (international) and NEC (North America).
Traditional fire alarm systems are not adequate in such environments because ignition risks are high, explosion hazards are present and detection time is critical. GST Addressable Fire Alarm Systems, when properly selected, certified and deployed, can help organizations achieve reliable protection in hazardous zones while ensuring compliance with ATEX and related industrial safety regulations.

This comprehensive guide explains how GST addressable systems can be implemented in hazardous zones, what standards must be met and the best practices that ensure safety and regulatory compliance.
1. What Are Hazardous Zones and ATEX Classifications?
A hazardous zone is any location where explosive atmospheres caused by gases, vapors, mists or dust may exist. These areas are commonly found in:
- Petrochemical and gas processing plants
- Oil and LNG storage terminals
- Paint and coating factories
- Power generation units
- Chemical and pharmaceutical sites
- Mining operations
- Food and grain processing plants
To manage risks, regulatory frameworks classify zones based on the likelihood of explosive atmospheres.
ATEX Zone Classifications (for EU & IECEx regions):
- Zone 0: Explosive atmosphere is continuously present or for long durations.
- Zone 1: Explosive atmosphere likely during regular operations.
- Zone 2: Explosive atmosphere unlikely and if it occurs, only for a short period.
Dust-Based Zones:
- Zone 20: Combustible dust is present continuously.
- Zone 21: Likely presence of dust during normal processes.
- Zone 22: Dust presence is infrequent and short-lived.
To operate in such zones, fire detection and alarm systems must use hardware that is explosion-proof, intrinsically safe and fully compliant with ATEX directives.
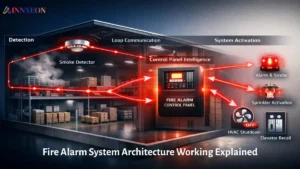
2. Why Choose GST Addressable Systems for Hazardous Zones?
GST addressable fire alarm systems are engineered to provide precise, intelligent and scalable detection across complex industrial settings. When deployed with explosion-proof and ATEX-certified devices, they offer several advantages:
- Accurate Device Identification: Each detector, manual call point and module has a unique address, enabling quicker fault isolation and event localization.
- Reduced False Alarms: Algorithms and digital communication help differentiate smoke, gas, steam and dust, minimizing false triggers that can halt production.
- Integration Compatibility: GST panels can interface with gas suppression systems, SCADA, BMS and emergency shutdown systems.
- Remote Monitoring & Control: Centralized control rooms can access alarms, fault logs and field device status in real time.
- Scalable Network Design: From a single production unit to an entire refinery or plant complex, the system supports zone expansion without major rewiring.
3. ATEX & Industrial Compliance Requirements
Before deploying GST systems in hazardous zones, organizations must meet the following compliance criteria:
✔ Equipment Certification
Fire detectors, call points, sounders and interfaces must be certified under:
- ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU
- IECEx international explosion-proof standards
- Local approvals (FM, UL, EN54, BIS, PESO, etc.)
✔ Intrinsic Safety (IS) Design
In areas with high explosion risk, circuits must use:
- Intrinsically safe (Ex i) barriers
- Flameproof enclosures (Ex d)
- Increased safety housings (Ex e)
✔ Cable and Wiring Compliance
Cables must be resistant to:
- Heat and temperature fluctuations
- Chemical exposure
- Flame and smoke propagation
- Physical and mechanical stress
✔ Installation Standards
Compliance with:
- NFPA 72
- EN 60079 series
- IS/IEC 60079
- BS 5839
✔ Maintenance Requirements
Regular ATEX-certified inspections and preventive maintenance routines are mandatory.
4. Components of a GST Addressable System for Hazardous Zones
A compliant setup typically includes:
- Explosion-Proof Smoke/Heat Detectors: Installed with flameproof enclosures where gas/vapor ignition is possible.
- Intrinsically Safe Manual Call Points: Fitted with sealed housings, conforming to IP66/IP67 standards.
- IS Sounders, Beacons & Siren Systems: These ensure safe alerting without generating sparks or heat.
- Addressable Control Panels: Panels like GST200, GST5000, or GST9000 (depending on project scale) support intelligent zoning and industrial integration.
- Line Isolators & Loop Interfaces: Protect loops from ground faults and voltage spikes.
- Zone Monitors: Link ATEX devices to the addressable system in compliance with zone-based isolation protocols.
5. Step-by-Step Deployment Process
Step 1: Site Assessment & Hazard Mapping
Map hazardous zones (0/1/2/20/21/22) and identify ignition risks, temperature classes and protection concepts.
Step 2: Device Selection
Use only:
- ATEX-certified detectors
- Intrinsically safe call points
- Compatible GST control panels
- Certified junction boxes and loop isolators
Step 3: Loop Design & Wiring
- Route cables through flameproof conduits
- Use galvanic IS barriers where needed
- Separate power and signal circuits
- Ensure loop integrity across zones
Step 4: Panel Programming
Assign unique addresses, configure zones and activate alarm verification logic.
Step 5: Testing & Commissioning
Perform:
- Loop continuity tests
- Earth leakage checks
- Spark safety verification
- Alarm simulations
Step 6: Documentation & Compliance Inspection
Maintain logs of equipment certification, loop drawings, device address sheets and inspection records.
6. Industry-Specific Use Cases
- Oil & Gas Refineries: Explosion-proof detectors installed in pump rooms, storage tanks, offshore rigs and gas compressor buildings.
- Chemical Processing Units: Addressable alarms integrated with gas suppression and emergency shutdown systems.
- Pharmaceutical Plants: Dust-prone areas use optical detectors paired with dust filters and IS modules.
- Power & Energy Facilities: Control rooms connected to SCADA for real-time supervision and automated isolation triggers.
- Paint, Varnish & Coating Units: Ex-proof call points and beacons installed near mixing and spray areas.
7. Best Practices for Compliance & Safety
To ensure long-term reliability in hazardous environments:
1. Use Only Certified Equipment
Always check ATEX, FM, IECEx, PESO or UL marks.
2. Implement Redundant Loops
Maintain operation even if one segment is compromised.
3. Protect Cables and Junctions
Use metal conduit, armored cable, or tray systems.
4. Perform Frequent Inspections
Inspect enclosures, barriers and field wiring at planned intervals.
5. Train Maintenance Teams
Educate technicians on handling IS devices and zoning protocols.
6. Align With Fire Safety Authorities
Comply with local fire departments, insurance agencies and government safety boards.
8. Challenges and How to Overcome Them
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Harsh environmental exposure | Use IP66/IP67 rated devices |
| Voltage drops in long loops | Implement addressable isolators and boosters |
| False alarms due to dust or vapors | Use heat/flame detectors with adaptive logic |
| Certification limitations | Coordinate with approved integrators |
| Integration with suppression systems | Use relay modules and fault monitoring |
9. Maintenance & Lifecycle Compliance
Even after installation, hazardous zone systems need constant monitoring:
- Annual compliance audits (ATEX/IECEx/NFPA)
- Routine loop testing and calibration
- Device-level health monitoring via control panels
- Firmware and logic configuration updates
- Replacement of damaged or expired components
GST addressable control panels provide real-time fault diagnostics, logs and loop management features that simplify long-term upkeep.
10. Benefits of Using GST Addressable Systems in Hazardous Zones
Here’s a quick overview of the advantages:
- Precise incident localization
- Early fire and gas detection
- Safe operation in explosive atmospheres
- Integration with SCADA/BMS/ESD
- ATEX & IECEx compliant hardware
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Intelligent alarm signaling
- Scalable and adaptable architecture
Deploying GST Addressable Systems in hazardous zones requires a structured approach, certified hardware and strict conformity with ATEX and industrial safety standards. When designed and installed correctly, these systems provide unmatched protection, fast detection and seamless integration with existing safety infrastructure.
From oil refineries to chemical processing units and dust-prone facilities, GST fire alarm solutions play a pivotal role in mitigating explosion risks while maintaining compliance and operational continuity.
Whether you are a system integrator, facility manager, fire safety consultant or safety compliance officer, implementing ATEX-certified GST Addressable systems is an investment in safety, reliability and long-term cost control.
Read Also: Implementing GST Addressable Fire Systems in Industrial Plants: Safety & Compliance Guide
Read Also: Choosing Between GST-IFP8, GST-200 & GST-5000: Model Comparison for Large Projects