Smart buildings are no longer futuristic concepts. They are today’s reality. From intelligent lighting and automated HVAC to access control and IoT-driven analytics, modern infrastructure depends on connected systems that work together in real time. At the centre of this transformation sits one of the most powerful technologies: CCTV surveillance.
But CCTV is no longer just about recording footage.
Today, it acts as a data engine, safety layer, operational tool and business intelligence platform for smart buildings and commercial campuses. When integrated with AI, edge computing, fire alarms and building management systems (BMS), CCTV becomes a core part of intelligent decision-making.

In this guide, we’ll break down:
- How CCTV powers smart infrastructure
- Why engineers rely on it beyond security
- Integration strategies for campuses
- Technical architecture best practices
Let’s dive in.
Smart CCTV as the Digital Eye of Intelligent Infrastructure
In traditional buildings, CCTV served a simple purpose: record and review incidents.
In smart buildings, it is now:
- Detects threats automatically
- Tracks occupancy
- Supports automation systems
- Generates operational insights
- Enables predictive maintenance
- Enhances emergency response
Instead of passive monitoring, CCTV systems now deliver proactive intelligence.
This shift changes CCTV from a cost centre into a strategic asset.
What Is Smart Building CCTV?
Smart building CCTV refers to IP-based, AI-enabled and network-connected surveillance systems that integrate with:
- Building Management Systems (BMS)
- Access control
- Fire alarm systems
- IoT sensors
- Analytics platforms
- Cloud dashboards
These systems:
- Process video locally (edge AI)
- Send metadata to servers
- Trigger automated actions
- Support centralised monitoring
In simple terms:
Smart CCTV sees, understands and acts, not just records.
Why CCTV Is Critical for Smart Buildings
Let’s look at the core roles it plays.
1. Security & Threat Prevention
Security remains the primary use case.
Modern cameras can:
- Detect intrusions
- Identify suspicious behaviour
- Recognise faces or license plates
- Send instant alerts
- Trigger alarms automatically
This reduces response time drastically.
Instead of waiting for operators, AI flags threats instantly.
Example:
If someone enters a restricted server room:
- Camera detects an unauthorised presence
- System alerts security
- Access control locks doors
- Event recorded with timestamps
All within seconds.
2. Operational Intelligence
Here’s where CCTV becomes exciting for engineers.
Video data can reveal:
- Crowd density
- Space usage
- Queue lengths
- Peak occupancy
- Parking utilization
This helps facility teams:
- Optimize layouts
- Reduce energy waste
- Improve visitor flow
- Increase productivity
Example:
If meeting rooms stay empty 60% of the day, you can redesign or repurpose them.
CCTV provides measurable, actionable insights.
3. Energy Optimisation
Smart campuses aim to reduce energy consumption.
CCTV integrates with:
- Lighting control
- HVAC systems
- Motion sensors
If cameras detect no occupancy:
- Lights turn off
- Air conditioning reduces
- Energy costs drop
This automation delivers real savings.
Large campuses report 15–30% lower energy usage after intelligent integration.
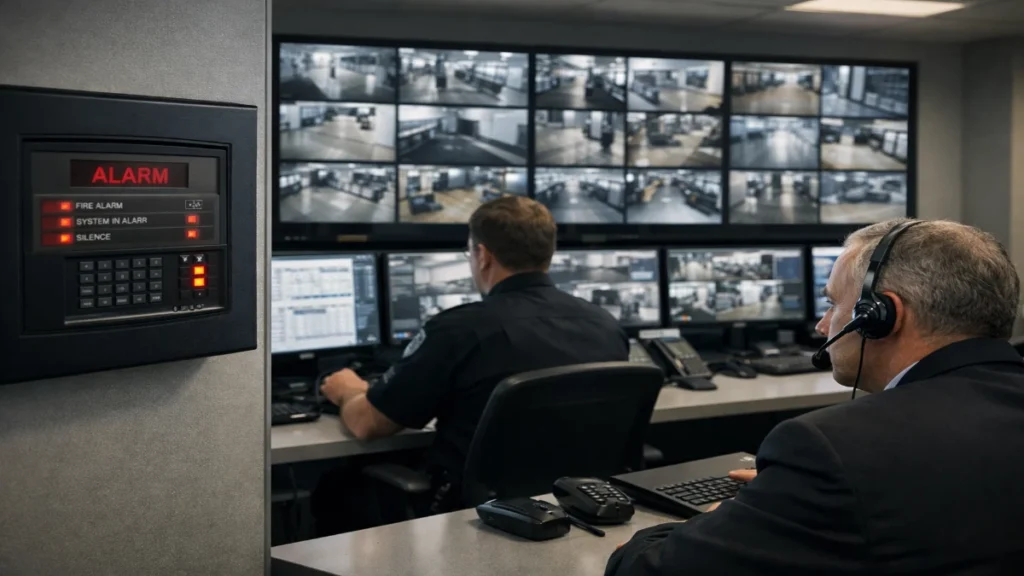
4. Safety & Emergency Response
CCTV significantly improves emergency handling.
During:
- Fire events
- Medical emergencies
- Evacuations
- Security breaches
It provides:
- Real-time visuals
- Situation awareness
- Faster coordination
- Safer evacuation routes
Integration Example:
When a fire alarm triggers:
- Cameras near the zone pop up automatically
- Security sees the exact situation
- PAVA announces evacuation
- Operators guide responders
This coordination saves lives.
5. Compliance & Audit Readiness
Many industries require:
- Video evidence
- Incident documentation
- Access tracking
- Regulatory reporting
CCTV ensures:
- Timestamped recordings
- Secure storage
- Easy retrieval
- Legal compliance
Especially for:
- Hospitals
- Airports
- Data centers
- Manufacturing plants
- Government campuses
Without CCTV, compliance becomes difficult.
Technical Architecture of Smart CCTV Systems
Understanding the architecture helps engineers design better systems.
Core Components
Cameras
- IP-based
- PoE powered
- 4K/8MP resolution
- Edge AI capable
Edge Devices
- Local analytics
- Faster decisions
- Reduced bandwidth
Network Infrastructure
- VLANs
- Fiber backbone
- Redundant switches
VMS (Video Management System)
- Central control
- Recording
- Playback
- AI integration
Cloud/Hybrid Storage
- Backup
- Scalability
- Remote access
Analytics Layer
- Face recognition
- Heat mapping
- Behavior analysis
- Predictive alerts
Integration with Other Smart Systems
CCTV + Access Control
Benefits:
- Visual verification of entries
- Anti-tailgating detection
- Biometric confirmation
CCTV + BMS
Benefits:
- Occupancy-based HVAC control
- Smart lighting
- Energy savings
CCTV + Fire Alarm
Benefits:
- Automatic camera pop-up
- Faster incident analysis
- Reduced false alarms
CCTV + AI/IoT
Benefits:
- Real-time insights
- Predictive alerts
- Data-driven decisions
Integration turns isolated tools into one intelligent ecosystem.
AI & Edge Analytics: The Game Changer
AI transforms CCTV from reactive to predictive.
Common AI Features
- Face recognition
- Vehicle detection
- Intrusion alerts
- People counting
- Heat maps
- Object left behind detection
Why Edge AI Matters
Edge processing:
- Reduces latency
- Saves bandwidth
- Improves privacy
- Speeds up alerts
Instead of sending all video to the cloud, only important metadata travels.
This makes systems faster and scalable.
Use Cases in Commercial Campuses
Corporate Offices
- Visitor management
- Workspace optimization
- Security
IT Parks
- Access control integration
- Parking analytics
- Night monitoring
Universities
- Student safety
- Crowd management
- Event monitoring
Healthcare
- Patient protection
- Restricted zone surveillance
- Compliance
Manufacturing
- Safety monitoring
- Process observation
- Loss prevention
Each environment benefits differently, but the foundation remains the same: intelligent surveillance.
Best Practices for Engineers
If you’re designing a smart CCTV system, follow these:
1. Use IP-based architecture
Avoid analog. IP enables scalability.
2. Plan bandwidth carefully
Video traffic is heavy. Use VLANs and QoS.
3. Deploy edge analytics
Reduce server load.
4. Integrate early
Design CCTV with BMS and access control from day one.
5. Ensure cybersecurity
Encrypt feeds, secure firmware, and use strong passwords.
6. Focus on privacy compliance
Mask faces where required. Follow local regulations.
7. Choose scalable storage
Hybrid cloud models work best.
The Future of CCTV in Smart Buildings
What’s next?
Expect:
- 100% AI cameras
- Cloud-native VMS
- Digital twins
- Predictive security
- Autonomous incident response
Soon, CCTV systems will not just report problems.
They will solve them automatically.
Buildings will become:
- Safer
- Smarter
- More efficient
- Data-driven
And CCTV will remain the core intelligence layer.
Note: CCTV has evolved far beyond surveillance.
It now drives:
- Security
- Safety
- Energy efficiency
- Operational intelligence
- Compliance
- Automation
For smart buildings and commercial campuses, CCTV is not optional.
It is foundational.
If you want intelligent infrastructure, you must start with intelligent vision systems.
Because what a building can see, it can optimise.
And what it can optimise, it can improve.
That’s the true role of CCTV in the smart building era.
Read Also: Why Industrial CCTV Systems Are Designed Differently Than Commercial CCTV
Read Also: Enterprise CCTV Network Architecture: What IT Teams Expect